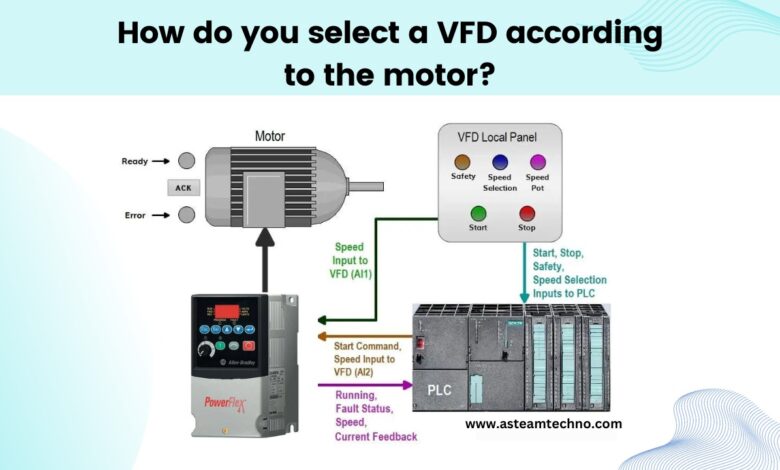
There are various important elements to take into account when choosing a Allen Bradley variable frequency drive (VFD) for a motor. The general steps to help you through the procedure are as follows:
Determine motor specifications:
Find out all the details you need about the motor, including its voltage, current rating, horsepower (HP), speed, and torque specifications. Usually, you may find these characteristics in the motor paperwork or on the nameplate of the motor.
- Consult motor documentation: Consult the motor’s documentation, such as the user manual or technical datasheet, if the nameplate does not contain all the relevant details. Specifications for the motor should be included in the documentation in great detail.
- Contact the manufacturer: You should get in touch with the motor manufacturer directly if you can’t find the necessary information or if you have any questions. Based on the model number or other identifying information, they ought to be able to help you determine the motor’s specs.
- Perform measurements: You might need to take direct measurements if the motor is not labelled or if the nameplate is damaged, missing, or unreadable. While the motor is operating or detached, measure the voltage, current, and resistance values using the proper tools, such as a multimeter or clamp metre. You may determine the motor’s specifications using these measurements.
Consider the motor type:
Find out what kind of motor you have, such as an induction motor, synchronous motor, or a particular motor design (like a permanent magnet motor). There might be special specifications for VFD compatibility for certain motor types.
- The most frequent kind of motors used in industrial applications are induction motors. Take the following factors into account when choosing a VFD for an induction motor.
- VFD Compatibility: Induction motors are compatible with the majority of common VFDs. However, make sure the VFD is compatible with the motor’s specified voltage and current ratings.
- Starting Method: There are two primary methods for starting induction motors with VFDs: scalar control (V/f control) and vector control. Although it could necessitate a more sophisticated VFD, vector control offers superior performance and torque control.
- Motor Protection: To protect the induction motor while it is operating, the VFD should have built-in motor protection features including overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal overload protection.
Determine the VFD capacity:
Based on the power needs of the motor, determine the VFD capacity. Make that the motor’s specs are suitable with the current and voltage ratings of the VFD. In general, the VFD’s current rating need to be on par with or greater than that of the motor.
- Calculate the motor power: Decide whether the motor’s power rating is expressed in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). This information can be found in the motor literature or on the nameplate of the motor. Use the conversion factor of 0.746 kW per HP if the motor is rated in HP to convert it to kW.
Also Reads :- Allen Bradley PowerFlex 4M AC drives
Assess the speed control requirements:
Find out what speed control abilities your application requires. While certain motors could need precise speed control, others might only need minimal control. Make sure the VFD you choose can deliver the appropriate speed range and control precision.
- Desired Speed Range: Establish the speed range that is necessary for your application. The minimum and maximum speeds that the motor must operate at are indicated by this. While some applications could call for precise speed control over a limited range, others might allow for a wider range of allowable speeds.
- Speed Regulation Accuracy: Take into account the degree of accuracy required for speed regulation in your application. While some applications, like robots or precision machining, may have more relaxed requirements, others may call for very strict speed control. Choose a VFD that can offer the appropriate level of control accuracy after determining the allowed level of speed variation.
Check for additional features:
Think about any new features or capabilities you might require. These could consist of braking capabilities, motor protection features, programmability, compatibility with other control systems, and communication interfaces (such Modbus, Ethernet).
Review manufacturer documentation:
To confirm that the chosen VFD is appropriate for your motor, review the paperwork, specifications, and technical datasheets provided by the VFD manufacturer. Pay attention to any particular guidelines or advice offered by the manufacturer.
- VFD Specifications: Look at the manufacturer’s specifications in detail. The voltage rating, current rating, power rating, frequency range, control mechanism (such as scalar control, vector control), and any additional features or functionalities are all included in this.
- Motor Compatibility: Check to see if the manufacturer specifically mentions compatibility with the particular motor types you are using, such as synchronous motors, permanent magnet motors, or induction motors. Make sure the motor type you have is compatible with the VFD’s design.
Seek expert advice if necessary:
Consult a competent specialist or a representative from the VFD manufacturer if you have questions regarding the selection procedure or a difficult motor application. Based on your unique needs, they can offer advice.
By considering these factors, you can select a VFD that is suitable for your motor, allowing for efficient and reliable control over motor speed and performance.




